What is Intel Thunderbolt? A Comprehensive Guide
Are you looking for a high-speed, versatile connection that can handle all your data transfer needs? Look no further than Intel What is Intel Thunderbolt! This powerful technology has been making waves in the tech world since its introduction in 2011. But what is Thunderbolt? How does it work? And why should you care about it? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll answer all these questions and more, giving you everything you need to know about Intel Thunderbolt and how to use it to take your computing experience to the next level. So grab a cup of coffee and get ready to learn!
What is Intel Thunderbolt?
What is Intel Thunderbolt? It is a high-speed data transfer technology developed by Intel that allows for lightning-fast connectivity between devices. It was first introduced in 2011 and has since become an industry standard, used in everything from laptops to desktops and even external hard drives.
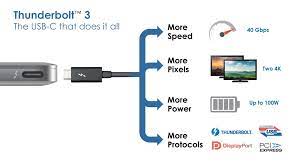
What makes What is Intel Thunderbolt so special? For starters, it boasts speeds of up to 40 Gbps (gigabits per second), making it one of the fastest connection technologies available today. This means that you can transfer large files, such as videos or photos, in seconds rather than minutes.
One of the unique features of Thunderbolt is its ability to support multiple types of connections at once. This means that you can use a single cable to connect your computer to a monitor, ethernet port, and other peripherals all at once!
Another advantage of Thunderbolt is its compatibility with USB-C ports. Many newer laptops now come equipped with USB-C ports which are capable of supporting Thunderbolt technology.
Thunderbolt is an incredibly powerful and versatile connection technology that provides lightning-fast data transfer speeds while also allowing for easy connectivity between various devices.
The History of Thunderbolt
The history of What is Intel Thunderbolt? dates back to 2009 when Intel first introduced it as a high-speed data transfer technology. It was created in collaboration with Apple and aimed at providing faster connectivity options for Mac users.
Thunderbolt 1 was first launched in early 2011, offering data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps and the ability to daisy-chain multiple devices through a single port. The following year, Thunderbolt 2 was released, doubling the speed to 20 Gbps and improving display performance.
In late-2015, Intel unveiled Thunderbolt 3, which brought significant improvements over its predecessors. This version offered speeds up to 40 Gbps with support for dual-4K displays or one external monitor up to an impressive resolution of 5K.
Over the years, Thunderbolt has become increasingly popular among tech enthusiasts who require fast data transfer rates and high-resolution video output capabilities from their devices. Today you can find this technology not only on Apple products but also on Windows-based laptops and desktops from various manufacturers such as Dell and HP.
The history of Thunderbolt is marked by continuous innovation efforts aimed at improving speed, reliability, interoperability across different platforms while retaining backward compatibility with previous versions.
The Different Types of Thunderbolt Connections

Thunderbolt technology offers a range of connection options, each with varying capabilities and features. Thunderbolt 1 was the first iteration of this technology, offering up to 10 Gbps data transfer speeds per channel with two channels available for use.
Thunderbolt 2 followed soon after and featured an increase in speed up to 20 Gbps per channel and still maintained the same number of channels as its predecessor. This allowed users to daisy-chain multiple devices together while maintaining high-speed data transfer rates.
Next came Thunderbolt 3 which marked a significant improvement from previous versions by incorporating USB-C connectivity into the mix. The latest version can support dual-4K displays or one-digital display at resolutions up to 5K, making it highly versatile for video editing or gaming purposes.
In addition, Thunderbolt has also made strides in supporting PCIe expansion chassis that enable users to connect external graphics cards (eGPU) for enhanced gaming experiences on their laptops.
Thunderbolt connections offer fast and efficient data transfers that are ideal for professionals working in industries where large amounts of data need transferring quickly such as media production or IT sectors.
Pros and Cons of Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt is a revolutionary technology that offers high-speed data transfer rates and versatile connectivity options. However, like any other technology, it has its own set of pros and cons.
One of the biggest advantages of Thunderbolt is its speed. With transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, Thunderbolt can handle large files quickly and efficiently. This makes it ideal for professionals who work with large amounts of data such as video editors or graphic designers.
Another advantage of Thunderbolt is its versatility. It allows you to connect multiple devices through a single port, including displays, external hard drives, cameras and more. This results in fewer cables cluttering your workspace which leads to better organization.
However, one downside of Thunderbolt is cost. Devices supporting this technology are generally pricier than their counterparts without it which may be an issue for some people on a budget.
Another potential disadvantage is compatibility issues with older devices that don’t have USB Type C ports or Thunderbolt support built-in. Users may need adapters or converters which adds another layer of complexity when connecting devices together.
While there are both positives and negatives associated with using Intel Thunderbolt technology – the benefits outweigh the disadvantages overall by leaps and bounds making it one of the most popular technologies among modern digital users today!
How to Use Thunderbolt
Using Thunderbolt is relatively easy, especially if you have experience with other types of connections. First, ensure that both devices are Thunderbolt compatible and have the appropriate ports for connection.
Next, connect the two devices using a Thunderbolt cable. The cable should click into place once it is properly connected. If your device does not recognize the connection automatically, go to settings and select “Thunderbolt” as your preferred input method.
Once you’ve established a connection between devices through Thunderbolt, data transfer speeds can reach up to 40GBps! This means that large files such as videos or high-resolution images can be transferred quickly compared to traditional USB cables.
Additionally, it’s important to note that there are different types of Thunderbolt connectors available in the market today – some even allowing for daisy-chaining multiple devices!
Using Intel Thunderbolt technology is straightforward and hassle-free when connecting compatible devices together.
Conclusion
What is Intel Thunderbolt? is a revolution in data transfer technology that has changed the way we use our devices. It offers lightning-fast speeds, versatility, and ease of use.
Intel Thunderbolt is an impressive technology that makes it easy to connect your devices in new ways. With its high-speed data transfer rates and ability to handle multiple types of connections simultaneously, Thunderbolt has quickly become a must-have for anyone looking for top-of-the-line performance from their computers or laptops. Its future looks bright with developments such as the upcoming release of Thunderbolt 4 expected to bring even more improvements.
If you’re someone who needs fast and reliable data transfers between your devices or wants to take advantage of advanced display capabilities, then considering Thunderbolt-enabled options could be the best decision you make.




